The SCF ubiquitin ligase protein slimb regulates centrosome duplication in Drosophila |
| |
| Authors: | Wojcik E J Glover D M Hays T S |
| |
| Affiliation: | Department of Biology, Virginia Tech University, Blacksburg, Virginia, 24061, USA. ewojcik@vt.edu |
| |
| Abstract: | 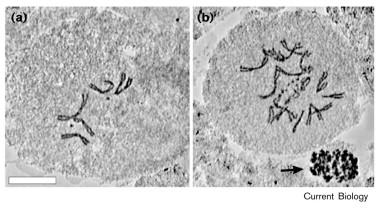
The duplication of the centrosome is a key event in the cell-division cycle. Although defects in centrosome duplication are thought to contribute to genomic instability [1-3] and are a hallmark of certain transformed cells and human cancer [4-6], the mechanism responsible for centrosome duplication is not understood. Recent experiments have established that centrosome duplication requires the activity of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (Cdk2) and cyclins E and A [7-9]. The stability of cyclin E is regulated by the ubiquitin ligase SCF, which is a protein complex composed of Skp1, Cdc53 (Cullin) and F-box proteins [10-12]. The Skp1 and Cullin components have been detected on mammalian centrosomes, and shown to be essential for centrosome duplication and separation in Xenopus [13]. Here, we report that Slimb, an F-box protein that targets proteins to the SCFcomplex [14,15], plays a role in limiting centrosome replication. We found that, in the fruit fly Drosophila, the hypomorphic mutation slimb(crd) causes the appearance of additional centrosomes and mitotic defects in mutant larval neuroblasts. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect PubMed 等数据库收录! |
|

