Exogenous dihydrosphingosine 1 phosphate mediates collagen synthesis in cardiac fibroblasts through JAK/STAT signalling and regulation of TIMP1 |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Cardiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, 109 Xueyuan Road, Wenzhou 25035, Zhejiang, China;2. Medical College of Zhejiang University City College, 51 Huzhou Road, Hangzhou 310000, China;3. Department of Cardiology, The Tongji Hospital of Tongji University, 309 Xincun Road, Putuo District, Shanghai 200065, China;1. Department of Neurosurgery, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200127, People''s Republic of China;2. Department of Cardiology, Longyan First Hospital affiliated to Fujian Medical University, Fujian 364000, People''s Republic of China |
| |
| Abstract: | 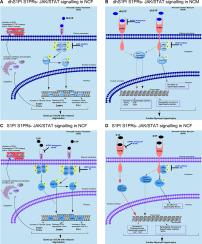
Cardiac fibrosis and myocyte hypertrophy are hallmarks of the cardiac remodelling process in cardiomyopathies such as heart failure (HF). Dyslipidemia or dysregulation of lipids contribute to HF. The dysregulation of high density lipoproteins (HDL) could lead to altered levels of other lipid metabolites that are bound to it such as sphingosine-1- phosphate (S1P). Recently, it has been shown that S1P and its analogue dihydrosphingosine-1-phosphate (dhS1P) are bound to HDL in plasma. The effects of dhS1P on cardiac cells have been obscure. In this study, we show that extracellular dhS1P is able to increase collagen synthesis in neonatal rat cardiac fibroblasts (NCFs) and cause hypertrophy of neonatal cardiac myocytes (NCMs). The janus kinase/signal transducer and activator (JAK/STAT) signalling pathway was involved in the increased collagen synthesis by dhS1P, through sustained increase of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP1). Extracellular dhS1P increased phosphorylation levels of STAT1 and STAT3 proteins, also caused an early increase in gene expression of transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ), and sustained increase in TIMP1. Inhibition of JAKs led to inhibition of TIMP1 and TGFβ gene and protein expression. We also show that dhS1P is able to cause NCM hypertrophy through S1P-receptor-1 (S1PR1) signalling which is opposite to that of its analogue, S1P. Taken together, our results show that dhS1P increases collagen synthesis in cardiac fibroblasts causing fibrosis through dhS1P-JAK/STAT-TIMP1 signalling. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

