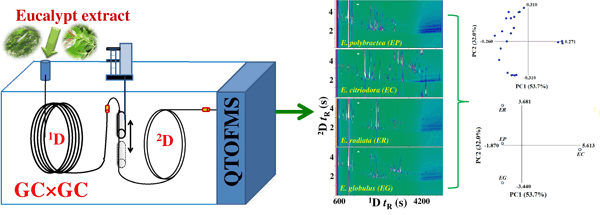
IntroductionChromatography with mass spectrometry (MS) is a technique of choice for metabolomic analysis of plant extracts. Single dimension gas chromatography (1DGC) with MS leads to poorly resolved metabolites of complex Eucalyptus spp. leaf oil secondary metabolites and consequently limited metabolic coverage of secondary compounds. Multidimensional chromatography with high resolution MS can contribute to advances in this field.ObjectivesDeeper insight into metabolite composition and variation for Eucalyptus spp. leaf oils through systematic untargeted metabolic profiling using comprehensive two-dimensional GC (GC?×?GC) with high resolution time-of-flight MS (accTOFMS), using generalised processes for metabolite identification.MethodsGC?×?GC separation used cryogenic modulation, with standard length polar first dimension and short fast analysis non-polar 2D columns. Compound tentative identification incorporated 1D and 2D retention information, retention indices, mass spectrum matching, and accurate mass MS data. Global metabolic profiles were interpreted through 2D contour plots and chemometric analysis.ResultsStrategies for metabolite screening and identification using GC?×?GC-accTOFMS were proposed. Considerably more components are detected and recognised than for 1DGC. Structured 2D molecular composition chromatographic patterns aid identification. ca. 400 metabolites were detected, 183 compounds were identified or tentatively identified, representing between 50.8–90.0% of the total ion count, comprising various chemical families. PCA revealed discriminating metabolites, allowing chemotaxonomic classification of species.ConclusionExpansion of metabolic coverage by using GC?×?GC-accTOFMS, and detailed 2D metabolic fingerprints of E. polybractea, E. citriodora, E. radiata and E. globulus leaf oils were established. This high resolution analytical platform, and identification strategy can be adapted to metabolic analysis of other plant extracts.Graphical abstractPhytoconstituents of four Australian eucalypt leaf oils were profiled using high resolution GC?×?GC-accurate mass TOFMS. Two-dimensional plots illustrated significant expansion of metabolic coverage. PCA discriminated metabolites of the eucalypts. |