
|
|||||
|
|
| Thermal stress,thermal safety margins and acclimation capacity in tropical shallow waters—An experimental approach testing multiple end-points in two common fish | |
| 摘 要: | 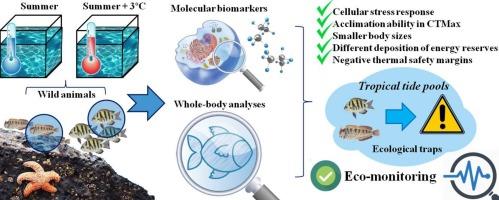 |
| 收稿时间: | 2017-03-02 |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! | |
 |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
| 设为首页 | 免责声明 | 关于勤云 | 加入收藏 |
|
Copyright©北京勤云科技发展有限公司 京ICP备09084417号 |