Challenges and opportunities in synthesizing historical geospatial data using statistical models |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Environmental Science, Policy, and Management, University of California, Berkeley, 130 Mulford Hall #3114, Berkeley, CA 94720-3114, USA;2. Department of Landscape Architecture and Environmental Planning, University of California, Berkeley, 230 Wurster Hall #1820, Berkeley, CA 94720-1820, USA;3. University of California Cooperative Extension, 5630 South Broadway, Eureka, CA 95503, USA;4. Seven Points Consulting, 900 San Bruno Ave, Brisbane, CA 94005, USA |
| |
| Abstract: | 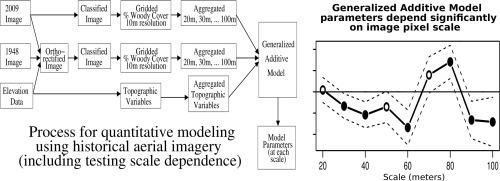
We classified land cover types from 1940s historical aerial imagery using Object Based Image Analysis (OBIA) and compared these maps with data on recent cover. Few studies have used these kinds of maps to model drivers of cover change, partly due to two statistical challenges: 1) appropriately accounting for spatial autocorrelation and 2) appropriately modeling percent cover which is bounded between 0 and 100 and not normally distributed. We studied the change in woody cover at four sites in California's North Coast using historical (1948) and recent (2009) high spatial resolution imagery. We classified the imagery using eCognition Developer and aggregated the resulting maps to the scale of a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) in order to understand topographic drivers of woody cover change. We used Generalized Additive Models (GAMs) with a quasi-binomial probability distribution to account for spatial autocorrelation and the boundedness of the percent woody cover variable. We explored the relative influences on current percent woody cover of topographic variables (grouped using principal component analysis) reflecting water retention capacity, exposure, and within-site context, as well as historical percent woody cover and geographical coordinates. We estimated these models for pixel sizes of 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, and 100 m, reflecting both tree neighborhood scales and stand scales. We found that historical woody cover had a consistent positive effect on current woody cover, and that the spatial autoregressive term in the model was significant even after controlling for historical cover. Specific topographic variables emerged as important for different sites at different scales, but no overall pattern emerged across sites or scales for any of the topographic variables we tested. This GAM framework for modeling historical data is flexible and could be used with more variables, more flexible relationships with predictor variables, and larger scales. Modeling drivers of woody cover change from historical ecology data sources can be a valuable way to plan restoration and enhance ecological insight into landscape change. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

