| Abstract: | 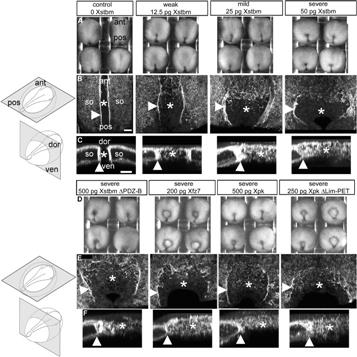
The noncanonical wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway [1] regulates the mediolaterally (planarly) polarized cell protrusive activity and intercalation that drives the convergent extension movements of vertebrate gastrulation [2], yet the underlying mechanism is unknown. We report that perturbing expression of Xenopus PCP genes, Strabismus (Xstbm), Frizzled (Xfz7), and Prickle (Xpk), disrupts radially polarized fibronectin fibril assembly on mesodermal tissue surfaces, mediolaterally polarized motility, and intercalation. Polarized motility is restored in Xpk-perturbed explants but not in Xstbm- or Xfz7-perturbed explants cultured on fibronectin surfaces. The PCP complex, including Xpk, first regulates polarized surface assembly of the fibronectin matrix, which is necessary for mediolaterally polarized motility, and then, without Xpk, has an additional and necessary function in polarizing motility. These results show that the PCP complex regulates several cell polarities (radial, planar) and several processes (matrix deposition, motility), by indirect and direct mechanisms, and acts in several modes, either with all or a subset of its components, during vertebrate morphogenesis. |

