In vitro and in vivo anticandidal efficacy of green synthesized gold nanoparticles using Spirulina maxima polysaccharide |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Environmental Sciences, School of Natural Resources and Environment, University of Birjand, Birjand, Iran;2. Department of Environmental Science, Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran;1. Department of Nanoscience and Technology, Alagappa University, Karaikudi 630 003, Tamil Nadu, India;2. Department of Botany, Alagappa University, Karaikudi 630 003, Tamil Nadu, India;3. Unit of Vector Control, Phytochemistry and Nanotechnology, Department of Zoology, Annamalai University, Annamalainagar 608 002, Tamil Nadu, India;4. School of Biosciences and Technology, VIT University, Vellore 632014, Tamil Nadu, India;5. Department of Botany and Microbiology, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh 11451, Saudi Arabia;6. Department of Agriculture, Food and Environment, University of Pisa, via del Borghetto 80, 56124 Pisa, Italy;7. The BioRobotics Institute, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Viale Rinaldo Piaggio 34, 56025 Pontedera, Pisa, Italy |
| |
| Abstract: | 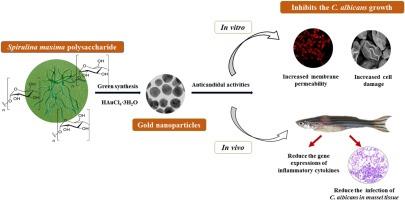
This study, for the first time, demonstrated an unprecedented approach for the green synthesis of gold (Au) nanoparticles (NPs) using the polysaccharide of Spirulina maxima as a reducing agent. Time-kill kinetic analysis was used to evaluate the antifungal activity of the green synthesized Au NPs against the pathogenic Candida albicans (C. albicans). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) were found to be 32 μg/mL and 64 μg/mL, respectively. Ultra-structural analysis indicated prominent damage on cell wall of the C. albicans after Au NPs treatment, and suggested that the treatment could increase the membrane permeability and disintegration of cells leading to cellular death. The results of propidium iodide (PI) uptake assay showed the higher level of cell death in Au NPs treated C. albicans cells, further confirming the loss of plasma membrane integrity. Cytotoxicity analysis of Au NPs on HEK293T and A549 cells showed no cytotoxic effect up to 64 μg/mL of Au NPs concentration, indicating the potential use in in vivo studies. Also, the recovery of C. albicans infected zebrafish after Au NPs therapy suggest green synthesized Au NPs from S. maxima polysaccharide as a prospective anticandidal agent. |
| |
| Keywords: | Gold nanoparticles Green synthesis Antifungal activity Biocompatibility |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

